
DownUnderCTF 2022
Nguồn ở đây nhá các bạn: 💀👆👆👆💀
Một giải CTF lần đầu tham gia của tôi và team tôi với những kiến thức tự học sau 1 thời gian. Với nhiều challenges của nhiều mảng, nhưng tôi sẽ viết bài dưới đây là mảng của tôi yêu thích và sẽ đi theo đó là RE, một mảng rất cần cơ bản như ngôn ngữ assembly x86/x64 nhá😁
Sau đây tôi vào việc đây, nay thời tiết ở Nga như bao ngày í ì y lạnh)))🥶 à mà có lò sưởi thế là nóng lắm mn» mà thôi gét gô🤪
1: source provided (Solved)

Thử thách đầu tiên là beginner thế nên tôi tin là nó sẽ không quá khó nhỉ
Tôi tải các file về và mở file chall.S:
SECTION .data
c db 0xc4, 0xda, 0xc5, 0xdb, 0xce, 0x80, 0xf8, 0x3e, 0x82, 0xe8, 0xf7, 0x82, 0xef, 0xc0, 0xf3, 0x86, 0x89, 0xf0, 0xc7, 0xf9, 0xf7, 0x92, 0xca, 0x8c, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xff, 0x89, 0xff, 0x93, 0xd1, 0xd7, 0x84, 0x80, 0x87, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0xd8, 0x97, 0x89, 0x94, 0xa6, 0x89, 0x9d, 0xdd, 0x94, 0x9a, 0xa7, 0xf3, 0xb2
SECTION .text
global main
main:
xor rax, rax
xor rdi, rdi
mov rdx, 0x32
sub rsp, 0x32
mov rsp, rsi
syscall
mov r10, 0
l:
movzx r11, byte [rsp + r10]
movzx r12, byte [c + r10]
add r11, r10
add r11, 0x42
xor r11, 0x42
and r11, 0xff
cmp r11, r12
jne b
add r10, 1
cmp r10, 0x32
jne l
mov rax, 0x3c
mov rdi, 0
syscall
b:
mov rax, 0x3c
mov rdi, 1
syscall
Đây là file được viết dưới dạng asm x86, do đó ta đi vào đọc xem thế nào nhé
SECTION .data ; đây là mảng các số có thể để sử dụng nó để tạo thành flag
c db 0xc4, 0xda, 0xc5, 0xdb, 0xce, 0x80, 0xf8, 0x3e, 0x82, 0xe8, 0xf7, 0x82, 0xef, 0xc0, 0xf3, 0x86, 0x89, 0xf0, 0xc7, 0xf9, 0xf7, 0x92, 0xca, 0x8c, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xff, 0x89, 0xff, 0x93, 0xd1, 0xd7, 0x84, 0x80, 0x87, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0xd8, 0x97, 0x89, 0x94, 0xa6, 0x89, 0x9d, 0xdd, 0x94, 0x9a, 0xa7, 0xf3, 0xb2
SECTION .text
global main
main: ; đi vào hàm nào
xor rax, rax ; rax = 0
xor rdi, rdi ; rdx = 0
mov rdx, 0x32 ; rdx = 0x32
sub rsp, 0x32 ; rsp = rsp - 0x32
mov rsp, rsi
syscall
mov r10, 0 ; r10 = 0
l:
movzx r11, byte [rsp + r10] ; có lẽ cái này nó là input đầu vào
movzx r12, byte [c + r10] ; còn cái này .data c
add r11, r10 ; input = input + r10 (khả năng add với index của nó)
add r11, 0x42 ; input = input + 0x42
xor r11, 0x42 ; input = input ^ 0x42
and r11, 0xff ; input = input & 0xff
cmp r11, r12 ; so sánh input với từng giá trị trong .data
jne b ; jump if not equal
add r10, 1 ; có thể hiểu ind++
cmp r10, 0x32 ; so sánh nó với 0x32
jne l ; jump if not equal
mov rax, 0x3c
mov rdi, 0 ; return 0 (thỏa mãn)
syscall
b:
mov rax, 0x3c
mov rdi, 1 ; có thể hiểu là return 1 (lỗi)
syscall
Từ phân tích trên thì ta thấy rõ bài này sẽ yêu cầu ta nhập input flag rồi rồi mã hóa từng kí tự của input đem so sánh với c
Với bài này chỉ sử dụng toán tử xor, and, add nên tôi sẽ đảo ngược lại quá trình nó với c là đầu vào và print kết quả nhận được.
Và đây là source Python tôi code để tạo flag:
c = [0xc4, 0xda, 0xc5, 0xdb, 0xce, 0x80, 0xf8, 0x3e, 0x82, 0xe8, 0xf7, 0x82, 0xef, 0xc0, 0xf3, 0x86, 0x89, 0xf0, 0xc7, 0xf9, 0xf7, 0x92, 0xca, 0x8c, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xff, 0x89, 0xff, 0x93, 0xd1, 0xd7, 0x84, 0x80, 0x87, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0xd8, 0x97, 0x89, 0x94, 0xa6, 0x89, 0x9d, 0xdd, 0x94, 0x9a, 0xa7, 0xf3, 0xb2]
flag = []
for i, x in enumerate(c):
b = ((x ^ 0x42) - 0x42 - i) % 256
flag.append(b)
print(bytes(flag).decode())
Và chạy nó ta nhận được flag: DUCTF{r3v_is_3asy_1f_y0u_can_r34d_ass3mbly_r1ght?}
Và chúc mừng ta đã hoàn thành xong task đầu tiên nhá.
2: Legit App Not Ransomware (Solved)
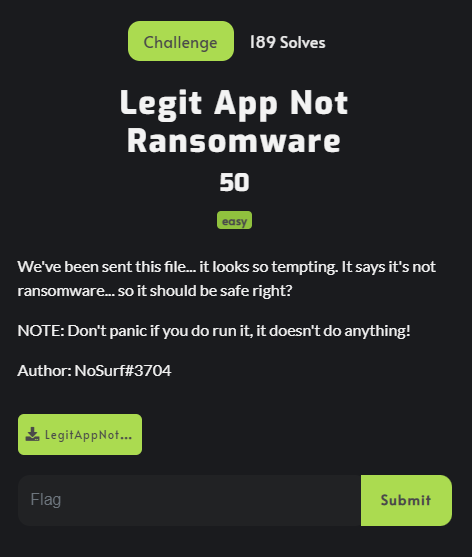
Kết quả tôi chạy thử chương trình:
Ta nhận được kết quả là yêu cầu ta chạy trên nền tảng .NET, do đó ta có thể sử dụng các phầm mềm như dotPeek, ilspy, dnSpy,…
Tôi sẽ chạy chương trình bằng dotPeek, tìm kiếm strings và các hàm, để xem hàm main ở đâu và thực hiện gì:
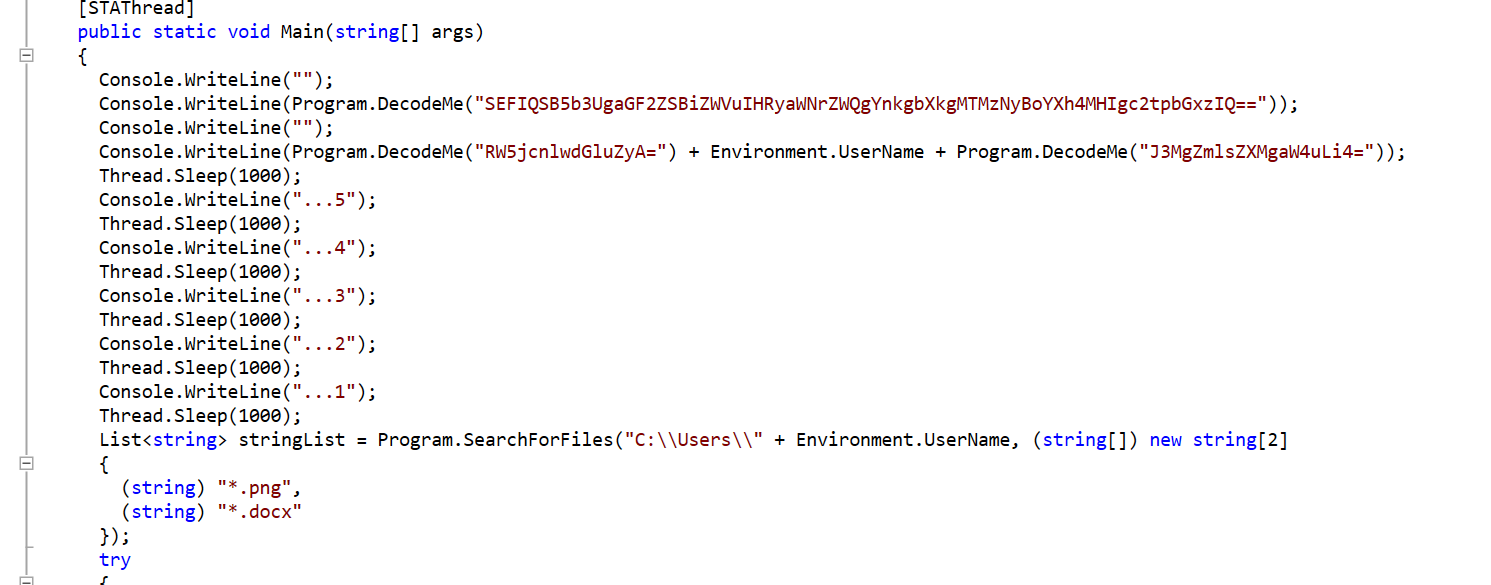
Dưới đây là code của toàn chương trình khi dotPeek giải cho ta:
using Microsoft.VisualBasic.CompilerServices;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
namespace LegitAppNotRansomware
{
[StandardModule]
internal sealed class Program
{
private static string a = "d3Jvbmdv";
private static string b = "aHR0cHM6Ly9iaXQubHkvM05SMkVvYg==";
private static string c = "OXdZV";
private static string d = "UkZWRFZF";
private static string e = "J1mM7";
private static string f = "elgyTjFZM1Z0WWpOeWZRPT0";
private static string g = "4n680y";
private static string h = "VHlwZSAhZmxhZyBpbiBkaXNjb3JkIGZvciB0aGUgU0VDUkVUIEVORElORw==";
private static string i = "SG93IG1hbnkgdGltZXMgd2lsbCB5b3UgdXNlIFJTQSBpbiB0aGUgd29ya3BsYWNlPyA6RA==";
private static string j = "KHNvbWUgb2YgdGhlc2UgZG9uJ3Qgd29yaywganVzdCBpZ25vcmUuLi5vciBtYXliZSBkb24ndD8p";
private static string l = "SGF2ZSB5b3Ugc3R1ZGllZCBmb3IgT1NDUCB0b2RheT8=";
private static string m = "aHR0cHM6Ly9iaXQubHkvM01sdmpSOQ==";
private static string n = "DUCTF{";
private static string o = "no}";
private static string p = "4n6grl";
private static string q = "RUFUIFNMRUVQIENURiBSRVBFQVQ=";
private static string r = "UmVkIFRlYW0gPiBCbHVlIFRlYW0=";
private static string s = "U3RhbmQgYmFjayBldmVyeW9uZSwgSSdtIGNlcnRpZmllZCE=";
private static string t = "zR4WTE4d2NsOWpNREJzWDJG";
private static string u = "WjdaREZrWDNrd2RW";
private static string v = "SVNPMjcwMDEgU0FWRSBVUw==";
private static string w = "Qmx1ZSBUZWFtID4gUmVkIFRlYW0=";
private static string x = "Z2hpZHJhIHNhdmUgbWUh";
private static string y = "QXJlIHlvdSBkZWNvZGluZyBhbGwgb2YgdGhlc2U/IFdoYXQgYSBjaGFtcCE=";
private static string z = "Password1";
[STAThread]
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine(Program.DecodeMe("SEFIQSB5b3UgaGF2ZSBiZWVuIHRyaWNrZWQgYnkgbXkgMTMzNyBoYXh4MHIgc2tpbGxzIQ=="));
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine(Program.DecodeMe("RW5jcnlwdGluZyA=") + Environment.UserName + Program.DecodeMe("J3MgZmlsZXMgaW4uLi4="));
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("...5");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("...4");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("...3");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("...2");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("...1");
Thread.Sleep(1000);
List<string> stringList = Program.SearchForFiles("C:\\Users\\" + Environment.UserName, (string[]) new string[2]
{
(string) "*.png",
(string) "*.docx"
});
try
{
foreach (string str in stringList)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}
finally
{
List<string>.Enumerator enumerator;
enumerator.Dispose();
}
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine(Program.DecodeMe("Li4uc28geW91IHdhbnQgdG8gZGVjcnlwdCB5b3VyIGZpbGVzPyBFbnRlciB0aGUgcGFzc3dvcmQ6IA=="));
Console.WriteLine("");
if (Operators.CompareString(Program.EncodeMe(Console.ReadLine()), Program.DecodeMe(string.Concat((string[]) new string[6]
{
(string) Program.d,
(string) Program.u,
(string) Program.c,
(string) Program.t,
(string) Program.f,
(string) "="
})), false) == 0)
Console.WriteLine(Program.DecodeMe("VGhhdCdzIGl0ISBUaGF0J3MgdGhlIGZsYWch"));
else
Console.WriteLine(Program.DecodeMe("V3JvbmcgcGFzc3dvcmQsIGxvb2tzIGxpa2UgeW91ciBmaWxlcyBhcmUgVE9BU1Q="));
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static List<string> SearchForFiles(string RootFolder, string[] FileFilter)
{
List<string> stringList = new List<string>();
Stack<string> stringStack = new Stack<string>();
stringStack.Push(RootFolder);
while (stringStack.Count > 0)
{
string str1 = stringStack.Pop();
try
{
string[] directories = Directory.GetDirectories(str1);
int index1 = 0;
while (index1 < directories.Length)
{
string str2 = directories[index1];
stringStack.Push(str2);
checked { ++index1; }
}
string[] strArray = FileFilter;
int index2 = 0;
while (index2 < strArray.Length)
{
string str3 = strArray[index2];
stringList.AddRange((IEnumerable<string>) Directory.GetFiles(str1, str3));
checked { ++index2; }
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ProjectData.SetProjectError(ex);
ProjectData.ClearProjectError();
}
}
return stringList;
}
public static string EncodeMe(string input) => Convert.ToBase64String(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(input));
public static string DecodeMe(string input) => Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(input));
}
}
Tôi thấy có hàm DecodeMe mở nó ra xem thì đây là hàm giải mã base64
public static string DecodeMe(string input) => Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(input));
Do đó tôi sẽ giải mã các đoạn strings của chương trình xem logic của bài sẽ như nào. Thì tôi phát hiện có hàm if kiểm tra flag:
Console.WriteLine(Program.DecodeMe("...so you want to decrypt your files? Enter the password: ");
Console.WriteLine("");
if (Operators.CompareString(Program.EncodeMe(Console.ReadLine()), Program.DecodeMe(string.Concat((string[]) new string[6]
{
(string) Program.d,
(string) Program.u,
(string) Program.c,
(string) Program.t,
(string) Program.f,
(string) "="
})), false) == 0)
Console.WriteLine("That's it! That's the flag!");
else
Console.WriteLine("Wrong password, looks like your files are TOAST");
Và thế là đã gần xong rồi, giờ chỉ cần nối các chuỗi d,u,c,t,f,"=" rồi giải mã nó là ra flag:
$echo RFVDVEZ7ZDFkX3kwdV9wYW4xY18wcl9jMDBsX2FzX2N1Y3VtYjNyfQ== | base64 --decode
Nhận được flag: DUCTF{d1d_y0u_pan1c_0r_c00l_as_cucumb3r}🫡
3: Clicky (Solved)
Đến với thử thách này chạy thì ta nhận thấy thông báo cần cài .NET, chứng tỏ là chương trình chạy trên nền tảng .NET
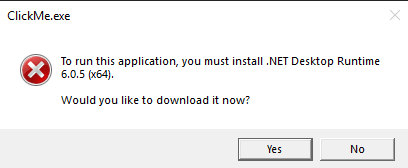
Thế thì ta tiếp tục mở bằng dotPeek và ta nhận được:
private void PictureBox1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.PictureBox1.Size.Height == 1)
{
int num1 = (int) MessageBox.Show("Here's the link! https://bit.ly/3MfBhmD");
}
if (this.PictureBox1.Size.Height == 10)
{
this.Timer1.Stop();
this.lbBossFight.ForeColor = Color.Green;
int num2 = (int) MessageBox.Show(string.Concat((string[]) new string[8]
{
(string) "How did you do this?!?! ",
(string) this.Unscramble("UkZWRFZFWT0="),
(string) this.Unscramble(this.flag),
(string) this.Unscramble(this.Random_function(this.Label1.Text)),
(string) this.Unscramble(this.Random_function(this.Label2.Text)),
(string) this.Unscramble(this.Random_function(this.Label3.Text)),
(string) "_ZGVhZGIzM2ZjYWZl",
(string) this.Unscramble(this.galf)
}));
}
if (this.PictureBox1.Size.Height == 75)
{
int num3 = (int) MessageBox.Show("You clicked me again! [EUROBEAT INTENSIFIES]");
this.PictureBox1.Size = new Size(10, 10);
this.DUCTF.Interval = 69;
this.lbBossFight.Text = "00:00:00";
this.lbWaterLevel.ForeColor = Color.Green;
}
if (this.PictureBox1.Size.Height != 100)
return;
int num4 = (int) MessageBox.Show("You clicked me! Time to get a bit smaller and faster!");
this.PictureBox1.Size = new Size(75, 75);
this.DUCTF.Interval = 420;
this.lbWaterLevel.Text = "00:00:00";
this.lbTutorial.ForeColor = Color.Green;
}
Tôi thấy đoạn mã này đáng nghi ngờ nên tôi sẽ lần tìm theo đó. Click kiểm tra hàm Unscramble và cả hàm Non_Random_function:
public string Unscramble(string input) => this.Non_Random_function(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(input)));
public string Non_Random_function(string input) => Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(input));
vâng 2 hàm này đại loại là giải mã base64 thông qua tham số truyền vào input. Ta đi vào hàm Unscramble tôi thấy nó dùng con trỏ this gọi hàm Non_Random_function -> input đầu vào của hàm Unscramble sẽ decode base64 2 lần.
-> UkZWRFZFWT0= return sau khi gọi hàm: DUCTF:
$ echo UkZWRFZFWT0= | base64 --decode | base64 --decode
DUCTF
Chắc là ta đi đúng đường rồi, tiếp tục thôi 🤪
Tiếp theo là this.flag và this.galf tương tự nó là { và }.
Ta đến với hàm Random_function:
public string Random_function(string input) => Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Convert.FromHexString(input));
Hàm này đơn giản chỉ là chuyển đổi từ hex sang chuỗi.
Ta thấy các Label1, Label2, Label3:
this.Label1.Text = "576B64736131677A62485A6B55543039";
this.Label2.Text = "57444E57656C70574F44303D";
this.Label3.Text = "57565935565646575453383D";
Giờ tôi đi 3 đoạn string này lên CyberChef ta nhận được kết quả:
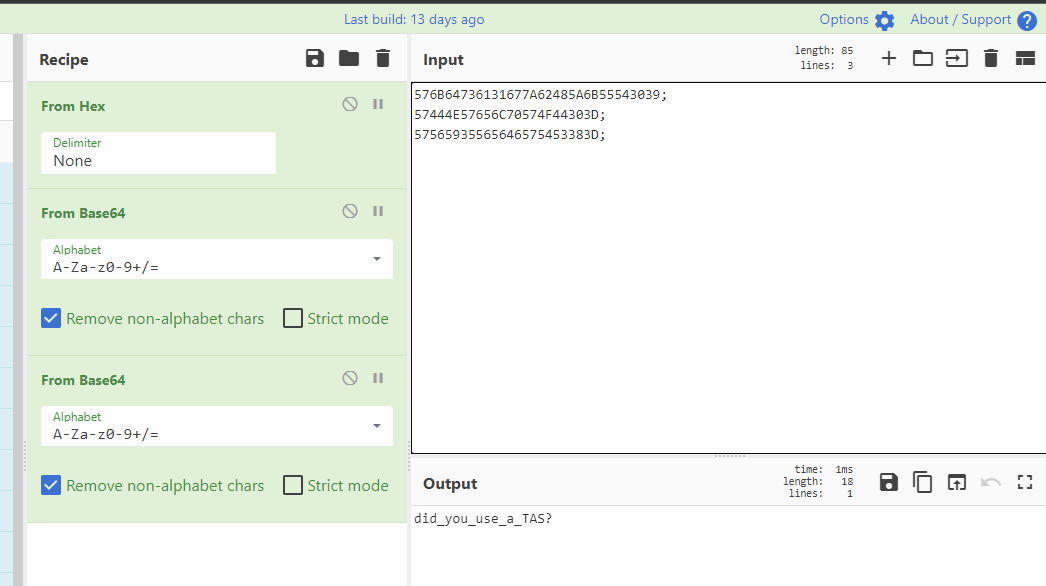
Và cơ bản là xong giờ ta chỉ gom vào là ta nhận được flag rồi:
DUCTF{did_you_use_a_TAS?_ZGVhZGIzM2ZjYWZl}
Vậy là xong challange 3 cũng khá dễ dàng nhé💀
4: js lock (Unsolved)
Với thử thách này là một thử thách liên quan đến js mở chương trình và phân tích một chút:🫡
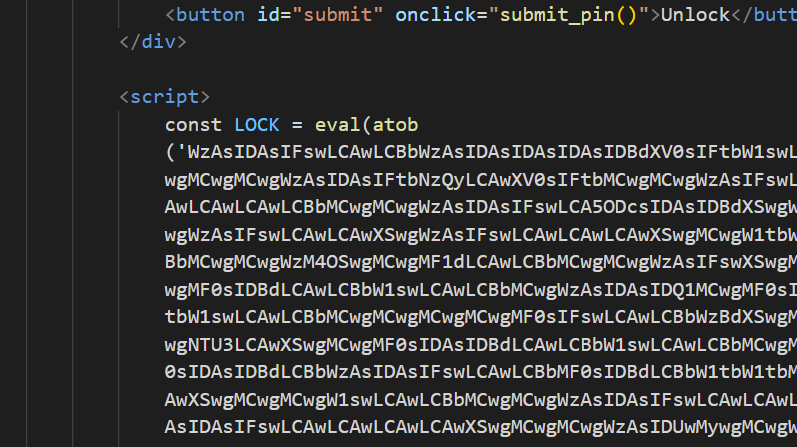
đây là lí do tôi không giải quyết được nhiệm vụ này là phân tích được các LOCK là gì????😥😪. Biến LOCK là một mảng lớn các số được lồng vào nhau.
Mở file này lên trình duyệt ta thấy giao diện có 3 nút 0 1 Unlock, chắc hẳn là ta cần mở khóa rồi rồi sẽ nó ra flag cho mình.
Đọc tiếp file vừa mở để hiểu được cơ chế nhận Flag
<html>
<body>
<script>
.... // đây là biến LOCK vì nó lớn quá lên k chép vào
const C = [62, 223, 233, 153, 37, 113, 79, 195, 9, 58, 83, 39, 245, 213, 253, 138, 225, 232, 123, 90, 8, 98, 105, 1, 31, 198, 67, 83, 41, 139, 118, 138, 252, 165, 214, 158, 116, 173, 174, 161, 6, 233, 37, 35, 86, 7, 108, 223, 97, 251, 2, 245, 129, 118, 227, 120, 26, 70, 40, 26, 183, 90, 172, 155]
function set_status(s) {
document.getElementById('status').innerHTML = s
}
function disable() {
document.getElementById('btn-0').disabled = true
document.getElementById('btn-1').disabled = true
document.getElementById('submit').disabled = true
}
function sha512(m) {
return crypto.subtle.digest('SHA-512', new TextEncoder('utf-8').encode(m))
.then((b) => new Uint8Array(b))
}
const S = { current: 1, key: '', T: LOCK, idx: 0 }
function hit_0() { //khi nhấn 0 thì key sẽ cộng thêm '0' và kiểm tra kiểu của S.T và giá trị xác định của S.T tại index hiện tại
S.key += '0'
if(typeof S.T != 'object' || S.T[S.idx] == undefined) {
set_status(`<div style="color: red">Pin ${S.current} is stuck!</div>`)
disable()
} else {
S.T = S.T[S.idx] // nếu tồn tại giá trị của S.T tại index thì S.T được gán giá trị của S.T tại index đó sau đó sẽ đặt lại giá trị của index = 0
S.idx = 0
document.getElementById('current-attempt').innerText = S.key
}
}
function hit_1() { //khi nhấn 1 thì s.key += '1'; index của s sẽ tăng lên 1
S.key += '1'
S.idx += 1
document.getElementById('current-attempt').innerText = S.key
}
function submit_pin() {
S.idx = 0 // gán giá trị cho index = 0
if(S.T === S.current) { // sẽ kiểm tra nếu giá trị mà nhấn hit_0 vừa xong mà bằng với giá trị s.current thì sẽ hiển thị đã unlockkkkkkk
set_status(`<div style="color: green">Pin ${S.current} unlocked!</div>`)
if(S.current == 1337) { // chuyển đến hàm nhận flag
win()
} else { // nếu không bằng 1337 thì current tăng lên 1 và tiếp tục .....
S.current += 1
document.getElementById("current-pin").innerText = S.current
S.T = LOCK
}
} else { // còn nếu không bằng thì sẽ dừng chương trình
set_status(`<div style="color: red">Pin ${S.current} didn\'t unlock!</div>`)
disable()
}
}
async function win() {
const K = await sha512(S.key) // K = chuỗi của sha512 của s.key nhận được mà ta trải qua đủ 1337 lần unlock
const dec = []
for(var i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
dec.push(String.fromCodePoint(C[i] ^ K[i])) // flag sẽ là kết quả của xor lần lượt từng bytes của K so với C tương ứng
}
const flag = dec.join('')
set_status(flag)
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Biến s được sử dụng để theo dõi trạng thái của khóa và được sửa đổi bất cứ khi nào chúng ta nhấn một trong các nút
Phải trải qua đủ 1337 lần unlock thì mới có flag (ban đầu current = 1, sau mỗi lần submit_pin thì sẽ được tăng 1 nếu pin đúng để mở màn).
Cái khó của bài này là ta làm sao để hit_0 và hit_1 làm sao đi vào được mảng lớn lồng nhau của LOCK để biết được index của nó là gì rồi từ đó ta hit_1 bấy nhiêu lần rồi hit_0 để gán giá trị rồi unlock để so sánh trả kết quả.
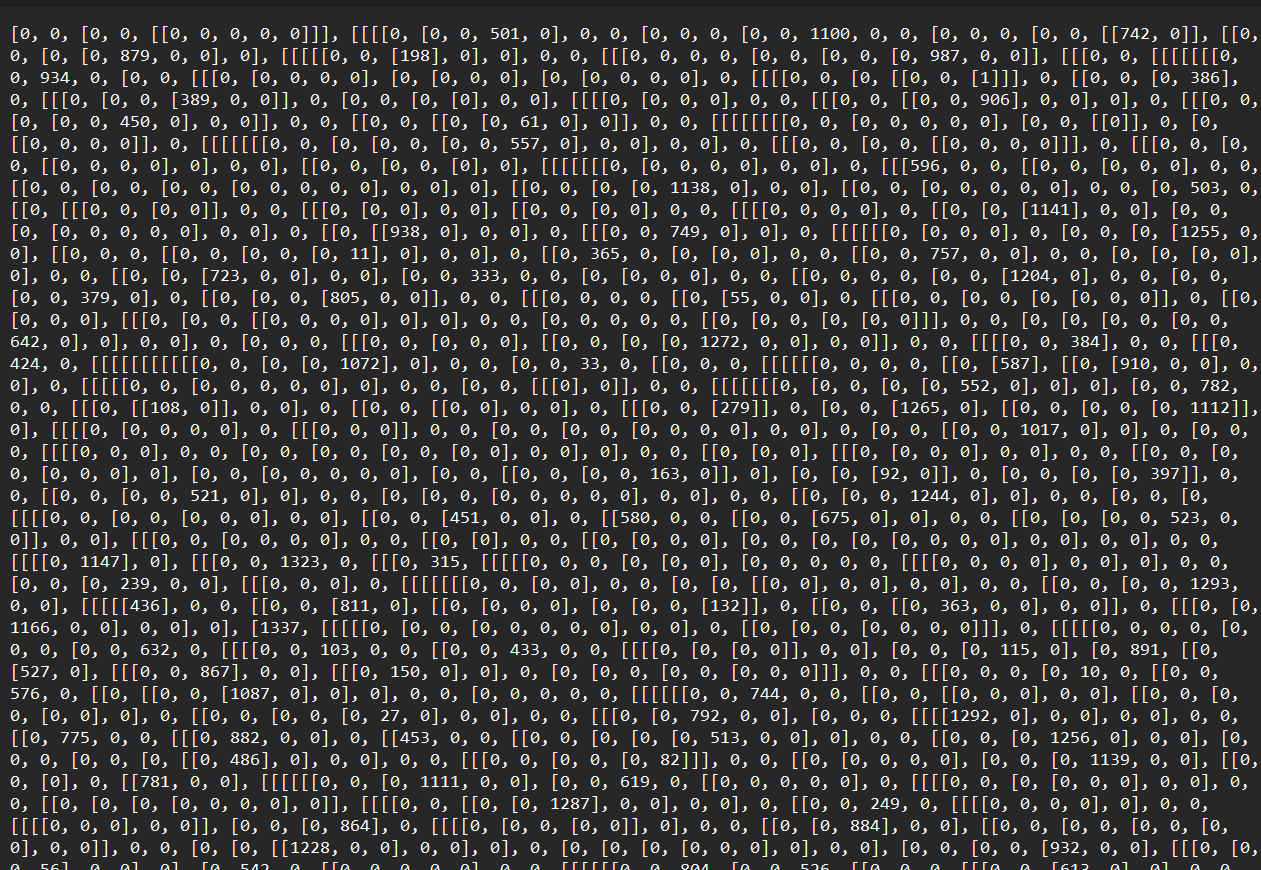
Ta thấy các số từ 1 -> 1337 được nằm dải rác ở trong tất cả các số 0. Ta nghĩ về các hàm hit_0 và hit_1 chuyển động trong mảng lớn. hit_1 đi qua phần tử tiếp thưo trong mảng, trong khi hit_0 sẽ chuyển qua một cấp độ sâu hơn trong mảng. Để mở khóa mỗi pin thì chúng ta phải chuyển động hit_1 và hit_0 để di chuyển đến các số theo thứ tự từ 1 đến 1337.
Dưới đây là ý tưởng của họ tải lên:
set_status = console.log;
const path_to_key = (path) => path.map(c => '1'.repeat(c) + '0').join('');
const paths = Array(1337);
function dft(s, path=[]) {
s.forEach((c, i) => {
const curPath = [...path, i];
if(typeof c === 'object') {
dft(c, curPath);
} else if(typeof c === 'number' && c !== 0) {
paths[c - 1] = path_to_key(curPath);
}
})
}
dft(LOCK);
S.key = paths.join('');
await win();
Chúng ta cùng phân tích nó để hiểu và thu nạp kiến thức nhé😁:
map()method được dùng khi bạn muốn thao tác trên 1 mảng và muốn trả về 1 mảng các giá trị thay đổi dựa trên giá trị của mảng đầu vàoforEach()method được dùng để lấy các phần tử trong mảng theo thứ tự và chuyển chúng đến hàm callback để xử lý. Vòng lặp trong forEach không thể dừng lại giữa chừng và số lần lặp sẽ luôn bằng với số phần tử có trong mảng ban đầu
Dưới đây ta sẽ phân tích cách giải nó nhé:
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(2**22)
from hashlib import sha512
from json import loads
from base64 import b64decode
LOCK = loads(b64decode(open('./LOCK.b64', 'rb').read()).decode()) #tạo biến LOCK (chép chuỗi dài ôi dồi vào file mới có tên LOCK.b64)
# vì LOCK đề bài cho bằng eval() -> nó mã hóa base64
ct = bytes([62, 223, 233, 153, 37, 113, 79, 195, 9, 58, 83, 39, 245, 213, 253, 138, 225, 232, 123, 90, 8, 98, 105, 1, 31, 198, 67, 83, 41, 139, 118, 138, 252, 165, 214, 158, 116, 173, 174, 161, 6, 233, 37, 35, 86, 7, 108, 223, 97, 251, 2, 245, 129, 118, 227, 120, 26, 70, 40, 26, 183, 90, 172, 155]) #từ đề bài
def find_key(T, k, path=''):
if T == k:
return path
if type(T) is list:
for i, t in enumerate(T):
r = find_key(t, k, path + '1'*i + '0')
if r:
return r
def check_key(h, k):
T = LOCK
idx = 0
for i in h:
if i == '1':
idx += 1
if i == '0':
T = T[idx]
idx = 0
return T == k
key = ''
for k in range(1, 1338):
h = find_key(LOCK, k)
key += h
assert check_key(h, k)
key = sha512(key.encode()).digest()
flag = bytes([a ^ b for a, b in zip(ct, key)])
print(flag.decode())
bytes()in python - return các đối tượng byte là một chuỗi các số nguyên, không thể thay đổi, được khởi tạo size và dữ liệu cho trước, trong phạm vi 0 <= x < 256.- Cú pháp:
bytes([source[, encoding[, errors]]]) - source: tự chọn
- encoding: tùy chọn, nếu nguồn là string thì đây là mã hóa của string đó
-
errors: tùy chọn, nếu nguồn là string, hành động sẽ được thực hiện khi quá trình bị lỗi
# Ví dụ: Chuyển đổi string thành byte: string = "Học Python trên quantrimang.com thật vui." #string với mã hóa 'utf-8' mang = bytes(string, 'utf-8') print(mang) #Nếu in từng phần tử có trong `mang` thì sẽ là vị trí của string đó trong bảng asccii 2# Ví dụ: Tạo mảng số nguyên với size cho trước: size = 5 mang = bytes(size) print(mang) #b'x00x00x00x00x00'
- Cú pháp:
-
bytearray()in python trả về một mảng byte với kích thước cho trước và các giá trị khởi tạo enumerate()in python thực sự có rất nhiều sức mạnh như:-
Hàm cho phép truy nhập vòng lặp lần lượt qua các thành phần của một collection trong khi nó vẫn giữ index của item hiện tại
names = ['Bob', 'Alice', 'Guido'] for index, value in enumerate(names): print(f'{index}: {value}') #output: #0: Bob #1: Alice #2: Guido -
Thay đổi starting index
names = ['Bob', 'Alice', 'Guido'] for index, value in enumerate(names, 1): print(f'{index}: {value}') #output: #1: Bob #2: Alice #3: Guido
-
Thế thôi vậy giờ qua file giải bằng python và nhận được flag: DUCTF{s3arch1ng_thr0ugh_an_arr4y_1s_n0t_th4t_h4rd_ab894d8dfea17}. Vâng nói chung thì đọc code thì khó khăn mỗi đoạn đi sâu vào mảng lớn 😪😪😪